
Safety
Spray Booth Decision-Making Tool
This resource addresses workplace safety concerns cited by IATSE 891 members.
In Spring 2022, IATSE 891 engaged Aura Health and Safety Corp and Ventilation Engineer Ed Chessor to meet with members to discuss, identify and work to address ongoing health and safety concerns common in Film and TV Production Workplaces.Concern: Spraying flammable and/or toxic products is dangerous.
If a Production is going to spray any type of chemical, whether it is a paint for Set Dec or fabric dye for Costumes Department, there are several regulations and codes that must be considered. These include WorkSafeBC Occupational Health and Safety Regulation as well as electrical and fire codes which set out requirements for spaces where paint is sprayed.Find in this document guidance to determine what type of Spray Booth is needed.
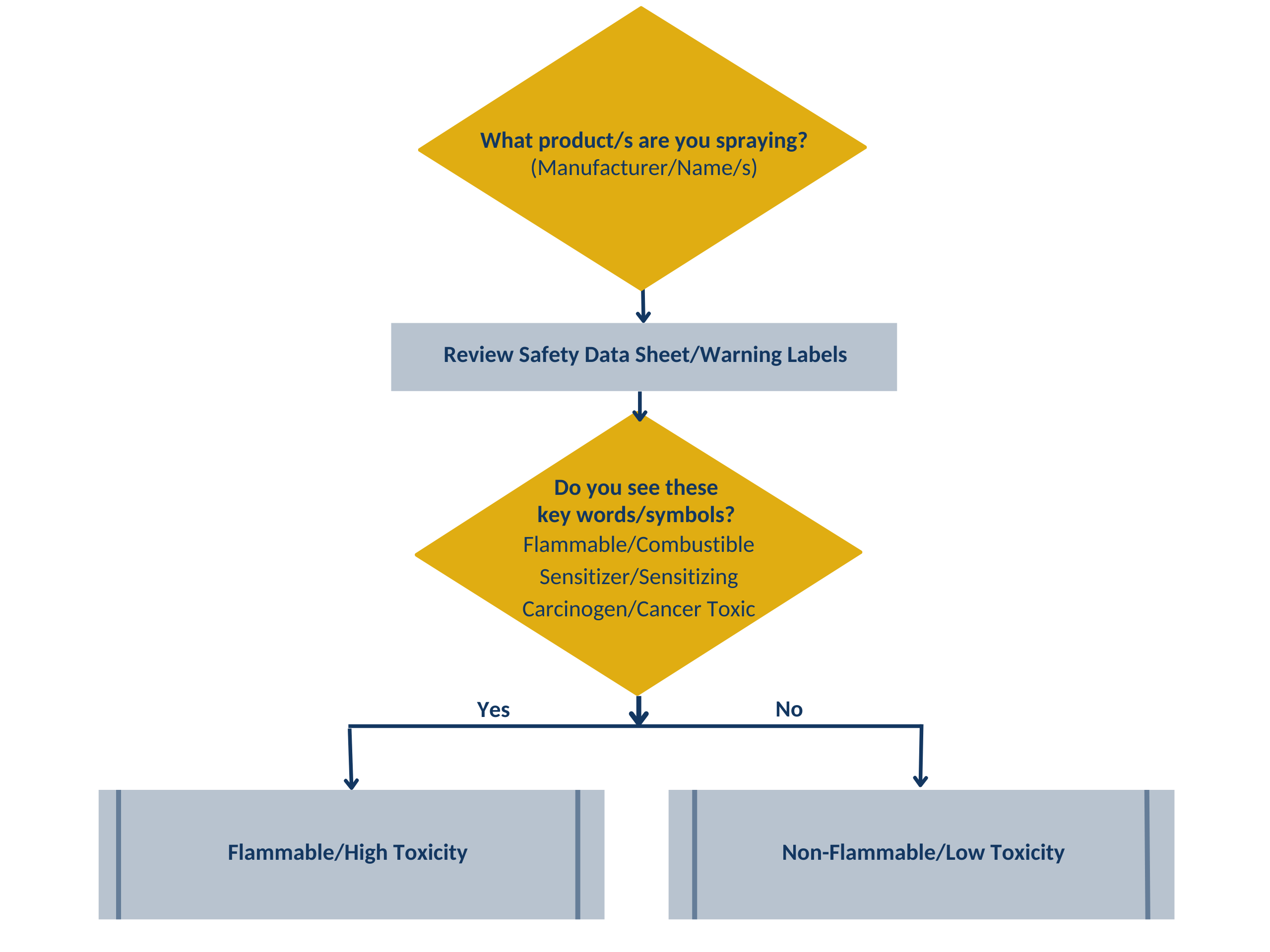
Needs will depend on what is being sprayed and space limitations. Take these steps:- See Flowchart I below - Determine the flammability and toxicity of the spray product(s).
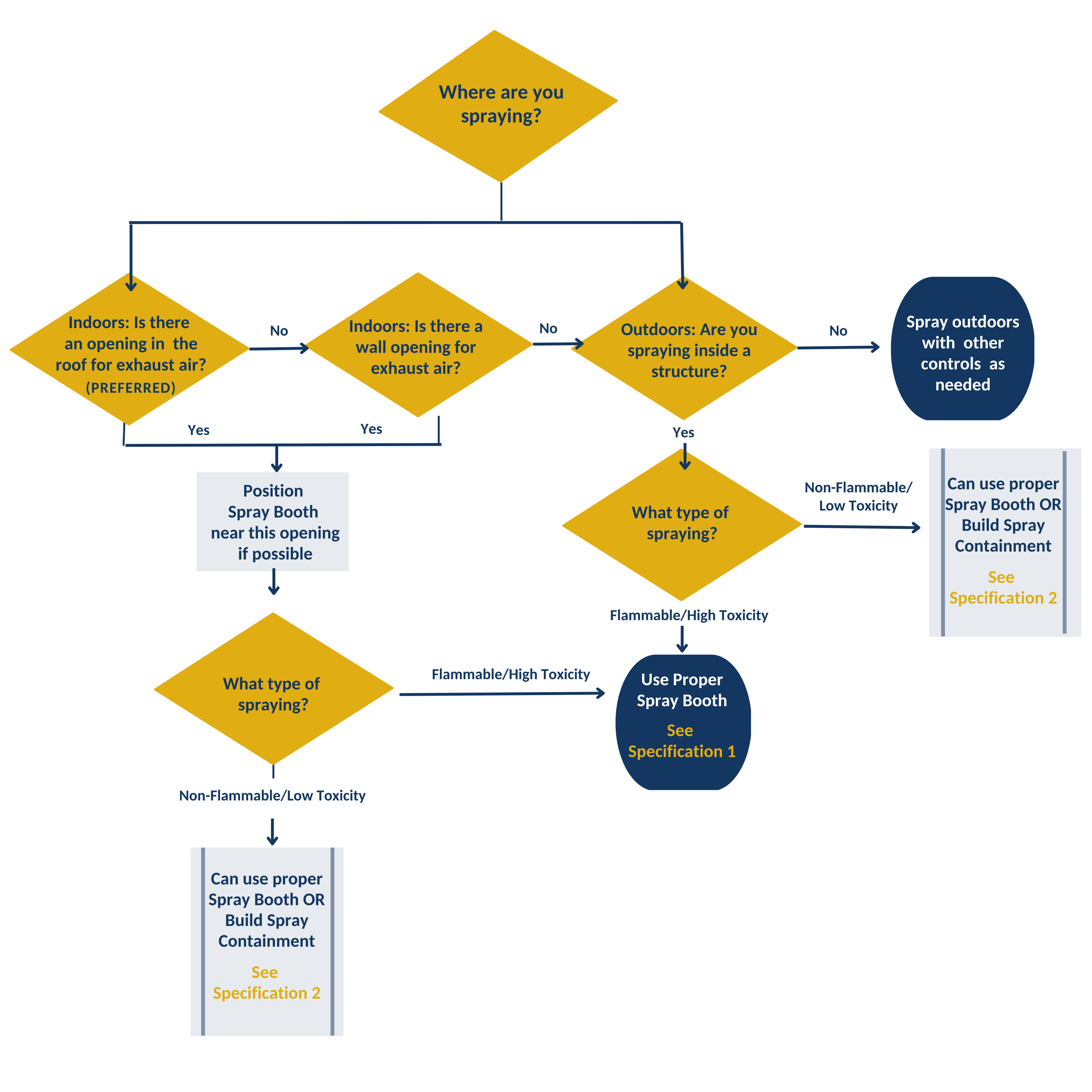
- See Flowchart II below - Determine what type of spray booth is needed.
- Follow Specification 1 or 2 - Consult one or the other specification as per assessed need.
DISCLAIMER: This resource is provided by IATSE 891 for informational purposes only. It is the responsibility of users to ensure that their controls and safeguards comply with applicable standards and guidelines e.g., Workers’ Compensation Act, and related Occupational Health and Safety Regulation, BC Fire Code, BC Building Code, BC Electrical Code, and Technical Safety BC.
Flowchart 1 - Determine flammability and toxicity of spray product(s)
Flowchart 2 - Determine type of spray booth needed
Specification 1 - Proper Spray Paint Booth
Use: For spraying paint e.g., for Set Dec and spraying costumes with flammable/higher toxicity products. IMPORTANT: Check Safety Data Sheets (SDS). Any spraying of two-part products (containing isocyanates or epoxy) must be conducted in a proper spray booth with airline respirators and other controls as per WorkSafeBC.| Specifications | There are two options:
|
| Location | Exhaust through building roof when possible. Or possibly locate shipping container outdoors with exhaust through the roof. |
| Tips for installation | Preferred - steel rigid ducting, spiral wound or welded. Many mill buildings have an exhaust fan with a roof opening 24 inches square or larger. You can move an existing fan aside to provide an opening for the spray booth stack. The booth can be relocated in a couple of days, making it practical for Productions to move to new locations, if needed. |
| Resources | Options for Spray Booths
|
Specification 2 - Local Exhaust Ventilation for Built Spray Booth/Area
Use: For spraying less toxic products (e.g., water-based dyes for costumes). For dipping or hand-painting activities. NOTE: Check Safety Data Sheets for information regarding flammability and toxicity.| Specifications | There are a few options:
|
| Location | Exhaust through building roof when possible. Or possibly locate space outdoors with exhaust through the roof. |
| Tips for installation | Preferred - steel rigid ducting, spiral wound or welded. Many mill buildings have an exhaust fan with a roof opening 24 inches square or larger. You can move an existing fan aside to provide an opening for the spray booth stack. Spray curtains should go up the roof. With ventilation, there will need to be make-up air. |
| Resources | Options for built booths |
ISSUED: January 18,2023 DISCLAIMER: This resource is provided by IATSE 891 for informational purposes only. It is the responsibility of any users to ensure that their controls comply with applicable standards and guidelines e.g., building and fire codes as well as occupational health and safety regulations.








